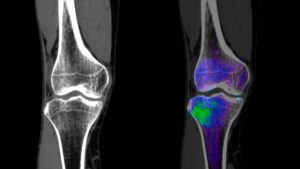
BONE MARROW EDEMA
If you suffer from Bone Marrow Edema, please Schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic specialists as soon as possible.
 What Is Bone Marrow EDEMA?
What Is Bone Marrow EDEMA?
Bone marrow edema results from the accumulation of excessive fluid within the bone marrow. This condition can be triggered by bone injuries, where the body initiates a protective response leading to fluid buildup. Additionally, underlying conditions like osteoporosis or tumors can contribute to bone marrow edema.
Within the bones, the bone marrow consists of spongy and flexible structures responsible for producing various types of blood cells, including red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. These blood cells play crucial roles in bodily functions such as oxygen transport, immune response to infections, and blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding from injuries.
Managing bone marrow edema involves addressing the underlying cause, whether it’s treating the bone injury, managing osteoporosis, or addressing the tumor. Depending on the severity and specific circumstances, medical interventions such as rest, medications, physical therapy, or surgical procedures may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
Causes Of Bone Marrow EDEMA
The cause of bone marrow edema is not fully understood, but experts attribute it to an imbalance in bone remodeling processes. It often occurs due to trauma, including acute injuries, fractures, or repetitive stress on the bone. Inflammatory conditions like arthritis or osteomyelitis may also play a role in its development. Another potential cause is avascular necrosis, where a lack of blood supply to the bone leads to tissue death and fluid accumulation.
Additionally, overuse or micro-trauma to the bone, commonly seen in athletes due to repetitive strain, can contribute to the onset of bone marrow edema. These factors disrupt the normal bone structure and fluid balance within the bone marrow, leading to symptoms such as pain, swelling, and decreased bone strength. Understanding these underlying causes deems crucial for developing effective treatment strategies aimed at alleviating symptoms and addressing the root cause of bone marrow edema.
Indications Of Bone Marrow EDEMA
The symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the specific location of the edema.
This condition commonly presents with localized pain in the affected bone, varying from dull, aching sensations to sharp discomfort. This pain typically worsens with weight-bearing or activity. Additionally, swelling and tenderness often show evident upon touch or pressure in the affected area. Depending on the bone marrow edema’s location, individuals may experience restricted range of motion or encounter difficulty with certain movements.
Doctors typically diagnose bone marrow edema through imaging studies, with MRI being the preferred modality due to its ability to clearly visualize changes in the bone marrow and surrounding structures. X-rays may also be employed to assess bone density and detect any associated fractures or abnormalities.
Treatments For Bone Marrow EDEMA
Rest and immobilization deem essential strategies to manage symptoms and facilitate healing of bone injuries. Avoiding activities that aggravate pain and providing adequate rest allow the bone to recover without additional stress. Pain management involves using over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications to alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation effectively.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in rehabilitation by incorporating specific exercises and stretches tailored by a physical therapist. These exercises aim to enhance range of motion, strengthen surrounding muscles, and promote healing of the affected bone. Depending on the severity of the injury, physicians recommend assistive devices such as crutches, braces, or other supports. This aims to minimize weight-bearing on the injured bone and support the healing process.
When bone injury deems secondary to an underlying condition like arthritis or avascular necrosis, treatment focuses on managing the underlying condition alongside addressing the bone injury. This holistic approach ensures comprehensive care to promote optimal recovery and long-term bone health.
In some cases, physicians may require more invasive interventions such as surgery or interventions. This aims to improve blood supply to the bone in cases of avascular necrosis.